In the modern industrial era, equipment reliability and efficiency are key factors in maintaining production continuity. One of the most effective approaches to achieving this is data-driven predictive maintenance, often referred to as data-driven maintenance. This approach utilizes operational data and equipment condition to predict potential failures before they occur, thus minimizing unexpected downtime.
What is Data-Driven Predictive Maintenance?
Data-driven predictive maintenance is a maintenance strategy that uses historical data, real-time sensors, and algorithmic analysis to determine when equipment is likely to experience performance degradation or failure.
Instead of performing periodic maintenance (time-based), this method determines the optimal maintenance time based on the actual condition of the equipment.
The data sources used can come from various monitoring systems, such as:
- Vibration sensors
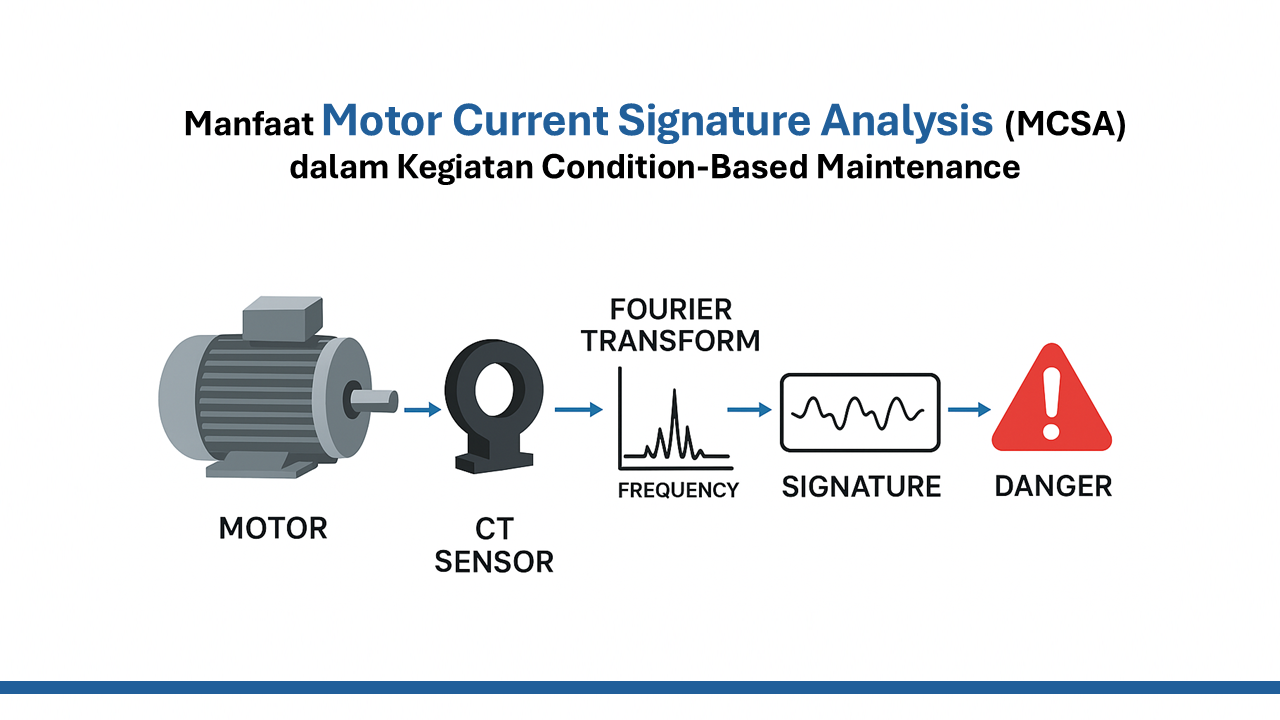
- Current and voltage measurements (Power Quality Spectrum)
- Temperature, humidity, and pressure
- Historical data from SCADA, IoT, or CMMS systems
Key Components of Data-Driven Maintenance
1. Sensors and Data Acquisition
Equipment is equipped with sensors that measure critical parameters such as vibration, temperature, current, and voltage. This data is collected continuously through IoT systems or data loggers.
2. Data Processing and Analysis
Raw data is processed into meaningful information through spectrum analysis, statistical algorithms, or machine learning.
For example, certain harmonic patterns in the Power Quality Spectrum can indicate bearing failure or rotor imbalance.
3. Predictive Models
These models use techniques such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) or Machine Learning (ML) to learn failure patterns from historical data and predict the time of the next failure.
4. Dashboard & Decision Support System
Analysis results are visualized in the form of graphs, trends, or machine condition alarms so that the maintenance team can make quick and accurate decisions.
Benefits of Data-Driven Predictive Maintenance
1. Reduced Unexpected Downtime
Potential disruptions can be identified long before fatal damage occurs.
2. Operational Cost Efficiency
Maintenance is only performed when absolutely necessary, rather than according to a fixed schedule.
3. Increased Equipment Lifespan
Timely intervention prevents further damage to components.
4. Improved Production Safety and Quality
Equipment that is consistently in optimal condition minimizes the risk of accidents and maintains production process stability.
Field Applications
- Electric motors and pumps: Harmonic and vibration analysis for early detection of misalignment or bearing wear.
- Generators and transformers: Current and voltage monitoring to detect phase imbalance or insulation damage.
- Mechanical equipment: Temperature and vibration trend analysis to predict mechanical failures.
One concrete example of implementation is the use of tools like Enging/Dynamox, which combines power quality spectrum analysis with vibration data to predict motor and generator failures.
Data-driven predictive maintenance is a strategic step towards an efficient, reliable, and sustainable smart industry. By relying on real-time data and analytical algorithms, companies can shift from reactive to proactive and predictive maintenance, thereby increasing productivity and optimizing operational costs.